Design and Develop
Product specification and design, technical development and qualification, the definition of product key characteristics, support to manufacturing and process design, technical changes and obsolescence management, technical operational documentation and manuals, instructions for continued airworthiness when applicable.
In support of the IAQG Standard 9115 Quality Management Systems – Requirements for Aviation, Space and Defense Organizations – Deliverable Software, the IAQG provides deployment support materials in the Core Guidance and Toolbox sections below.
The 9115 standard clarifies the 9100 quality management system requirements for deliverable software addressing activities from project planning through product delivery and maintenance. Deliverable software covered by 9115 may be stand-alone, embedded, or loadable into a target computer.
Areas within 9115 where clarifications of 9100 are concentrated include:
Infrastructure, Planning for Product Realization, Configuration Management, Security, Design and Development, Production and Service Provision, Control of Nonconforming Product,
And the introduction of customer application process guidance for:
-
- Design and development of Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) and Programmable Logic Devices (PLD).
- Simulation system software
- Test system software
- SCMH 2.2.2 Software Acronyms in Support of 9115 Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.3 Quality System Level Quality Planning and Implementation Guidance for Software Rev A Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.4 Organizational IA and Security Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.5 Organizational Software Auditing Considerations Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.7 Software Process Effectiveness Auditing Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.8 Project Level Considerations Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.9 Software Life Cycle Model Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.10 Defining Good Software Requirements Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.11 Software Measures and Metrics Rev B Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.12 Software Safety Rev A Dated 24MAR2020
- SCMH 2.2.13 Product Level Information Assurance and Security Rev A Dated 24MAR2020
The Notification of Change NOC training material is designed to assist organizations in executing a notification of a change in accordance with the IAQG Standard 9116. The material is provided in the form of an articulate training module that explains the use of the actual NoC Tool and the NoC Tool itself, created by the IAQG 9116 writing team.
This Change Impact Analysis Tool has been developed for use with IAQG Standard 9116 Notification of Change (NOC) Requirements (AS9116, SJAC9116 prEn9116). The purpose of the 9116 NOC Tool is to provide guidance for organizations to better understand when a NOC is to be completed in accordance with 9116 and how. The objective is to promote the benefits of the 9116 NOC Tool, to gain broader acceptance, whether or not the organization is required to use it, and to increase skills for those involved in managing design change notifications.
Early identification of customer implied special requirements or potential critical items provides valuable inputs to design engineering for their implementation, avoidance or elimination. Special Requirements and Critical Item (SRCI) control provides management with acceptance rationale for those requirements or items and identifies the means by which emanating risks can be controlled and mitigated. From this activity, critical design features, tests, inspection points, and procedures can be identified and implemented that will minimize the probability of failure of a product, mission or loss of life.
The concept of special requirements and critical items is interrelated in most of the paragraphs of the IAQG 9100 standard, thus implying they should be treated at all phases of the product lifecycle.
Since there is a relationship between Special Requirements and Critical Items identification and management and Risk Management methodologies, it is recommended that the reader be acquainted with Risk Management concepts and techniques. It is recommended to use the Risk Management guidance material in the SCMH Plan & Manage Section under Risk Management. Similarly, Critical Items control is often related to Key Characteristics variation management which is detailed in the SCMH Make Section under Product and Process Variation 9103.
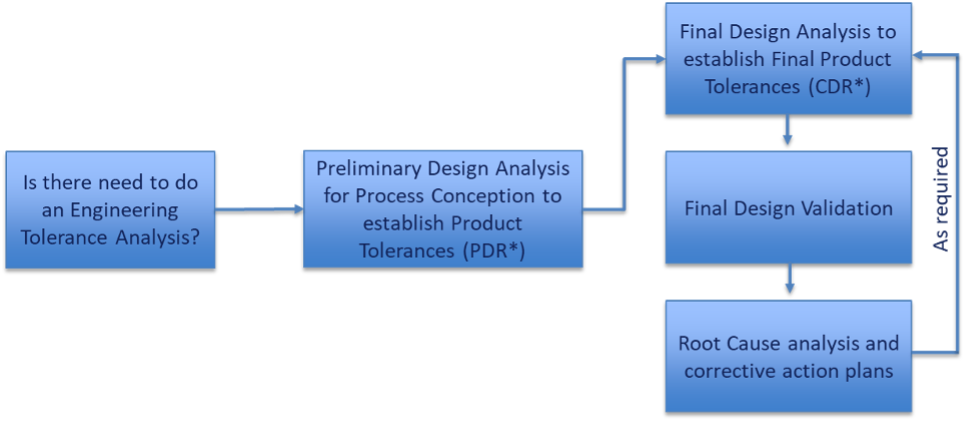
This guidance provides an understanding of the benefits and needs for Engineering Tolerance Analysis. It contains a flow chart for ETA with details for each element. The guidance provides various ETA Tools with some examples and calculations for;
- Worst Case Analysis
- Root Sum square formula (RSS)
- Benderizing Factor
- Gibson Factor
- Simulation (Monte Carlo)
IAQG standards AS/EN/JISQ/SJAC 9100, 9110 and 9120 require every organization to continuously improve their performances and determine actions to ensure these performances are in line with targets defined by internal and external stakeholders.
IAQG Product and Supply Chain Improvement Strategy Stream has identified a list of most commonly used Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) covering the main domains of the supply chain (‘Customer metrics’, ‘Engineering and Product Development’, ‘Program Management’, ‘Manufacturing and Production’, ‘Supplier Management’, and ‘In Service – feedback from operations’).
Use of these KPIs should support harmonization and reduction of customization of these KPIs between the entity establishing them and its different internal and external customers.
Each KPI is listed on a single page and provides the following information: KPI Name; KPI Abbreviation; KPI Description; KPI Formula; KPI Unit of measure; and Detailed explanations.
This guidance provides an understanding of Variation Sensitivity Analysis (VSA). It is the study of how the variation in the output of a model or system can be attributed to the variation of its inputs.
With an understanding that different sources of variation that combine to create an attribute have different levels of effect on the outcome of that attribute; a VSA returns value by discovering those differences. VSA determines which sources of variation have the greatest influence on the model and how to optimize tolerances to improve quality and reduce costs.
IAQG Standard 9145 applies Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) to the Aerospace industry. IAQG Standard 9145 introduces the concept of Design Risk Analysis (DRA) as an APQP deliverable. This guidance provides clarification of DRA and how an organization can apply DRA to a product design.
Webinars